Smart Mobility & Building

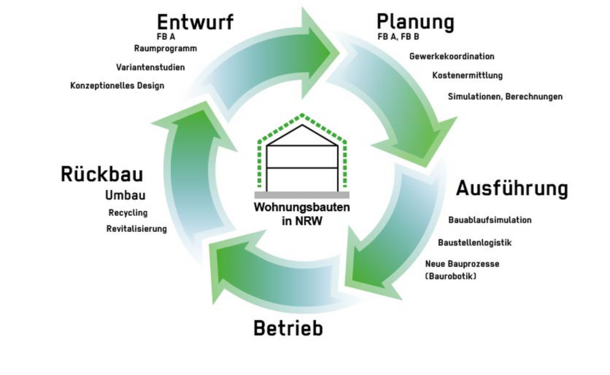
This research specialisation at Bochum University of Applied Sciences focuses on smart city approaches and in particular on smart solutions for the mobility and construction sectors. The researchers develop resource-efficient mobility concepts and modern building infrastructures as building blocks for a sustainable transport and energy transition at neighbourhood and city (district) level. This also includes projects on locally self-sufficient energy supply or storage technologies. Established topics include the development of solar vehicles and research into Electric Mobility and innovative digital methods such as Building Information Modelling (BIM). The research projects are national, but also have a strong European and international focus.
The research focus benefits from the cooperation between professorships and interdisciplinary institutions at Bochum University of Applied Sciences, such as the Institute for Electric Mobility, the Interdisciplinary Institute for Applied AI and Data Science Ruhr (AKIS), the BIM Institute (Building Information Modelling), the Laboratory for Sustainability in Technology and the Institute for Mobility and Transportation Systems.
In line with the university's sustainability profile, innovations that relate to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a particular focus. The focus is on inter- and transdisciplinary solutions that use applied research to find answers to urgent global challenges, as well as on sustainable local and regional solutions that preferably consider the entire life cycle of the approaches and innovations developed and promote sustainable individual behaviour.
Ongoing research projects on Smart Mobility & Building

Project management: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Friedbert Pautzke und Tobias Scholz, M.Sc.
Funding source: Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF)
Project executing organization: Bundesinstitut für Berufsbildung (bibb)
Funding programm: InnoVET
Duration: 2024 - 2027
Challenge
The need for skilled workers in trades and industry who are familiar with battery technologies, electromobility and hydrogen systems is constantly increasing. To successfully shape the energy and mobility transition, these skilled workers must continue their training in order to be able to develop and implement innovative technologies.
Solution
The task of the TraFuSMS project is to develop a modular educational concept that enables the needs-based training and further education of specialists for the energy and mobility transition. The focus is on three modules for specialists from automotive companies and industry as well as employees of start-ups and smaller companies in the field of sustainable mobility:
- Assessment of batteries in electric vehicles: This module enables learners and companies to carry out diagnostic and repair measures on electric vehicles and their energy storage systems.
- Innovation management in small companies: This promotes the entrepreneurial and innovation-oriented behavior of employees within the company.
- Working on hydrogen systems and developing sustainable energy systems: Learners are prepared to work safely on hydrogen systems and receive the knowledge to evaluate different energy systems and mobility solutions in terms of their sustainability.
The modular structure of the qualification also enables employees in start-ups or smaller companies to participate without having to be away from the company for long periods of time.
In addition, the use of intelligent, AI-based translation software is being tested to expand the content with English-language technical terms and thus prepare learners for documentation in English.
Transfer
The learning offer is to be certified by the Dortmund Chamber of Crafts (HWK) and the Bochum Moter Vehicle Trade Guild (KFZI) as well as the regional Chamber of Industry and Commerce (IHK) after successful testing. This certification strengthens the sustainability and recognition of the concepts in the industry.
After the project ends, the learning content developed will be included as educational offerings or to supplement training at the Chamber of Crafts and the Guild for the Automotive Trade. In addition, the technical teaching modules offer direct links to the energy industry, as energy storage devices from motor vehicles are reused as decentralized grid storage devices in households and industry.
Consortium
- Hochschule Bochum
- Electric Vehicle Institute
- DigiTeach Institute
- Resort studies, teaching and further training
- Dortmund Chamber of Crafts
- Bochum Moter Vehicle Trade Guild
Assoziiert
- Chamber of Industry and Commerce
- Bochum Economic Development
Further: Voltvogel, E-Adventures, ruhrvalley, Nüwiel



Project management: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Iris Mühlenbruch, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Sebastian Seipel
Funding source: Land NRW
Duration: 2024-2034 (Period of state funding)
The promotion of cycling is a key element of sustainable mobility and therefore an important concern of Bochum University of Applied Sciences. In view of the current shortage of skilled labour, which makes the planning and construction of cycling facilities more difficult, a new professorship for cycling is being established at Bochum University of Applied Sciences. This professorship is being funded by the state of North Rhine-Westphalia in order to support the training of urgently needed specialists and drive forward the transport transition.
The funding covers a period of ten years and provides up to 400,000 euros annually. In addition to funding the professorship itself, the funds also include the employment of two research assistants. These resources will enable Bochum University of Applied Sciences to expand its research and teaching in the field of cycling and at the same time make an important contribution to training new specialists at an academic level.
A key component of the funding is the establishment of a bicycle laboratory. The focus here is on expanding the consortium of survey and measuring equipment to ensure that theory and practice are closely linked in teaching and research. Students and researchers will have the opportunity not only to develop innovative solutions for cycling infrastructure, but also to test them under real-life conditions.
In addition to setting up the bicycle laboratory, Bochum University of Applied Sciences is planning to purchase materials for so-called reallife-laboratories. These reallife-laboratories are of great importance as they make it possible to test theoretically developed concepts in practice and thus strengthen the link to practice. In addition, reallife-laboratories act as an interface between research and the population by creating awareness and acceptance for innovative solutions in the field of cycling infrastructure. This actively involves the population in the development and implementation of new transport concepts.
In addition to the intensive teaching and research work at Bochum University of Applied Sciences, cooperation with neighbouring municipalities, particularly the city of Bochum, is another key aspect of the project. Through this cooperation, practice-orientated solutions are to be developed and implemented directly in the participating municipalities. This networking not only offers students valuable practical experience, but also enables local authorities to benefit from the latest scientific findings and realise innovative cycling solutions locally.
With the establishment of the cycling professorship and the associated measures, Bochum University of Applied Sciences and the state of North Rhine-Westphalia are providing significant impetus for the transport transition and making an important contribution to the training of specialists in the field of cycling. This represents a relevant milestone on the road to sustainable mobility and a future-proof transport infrastructure.
Further links:
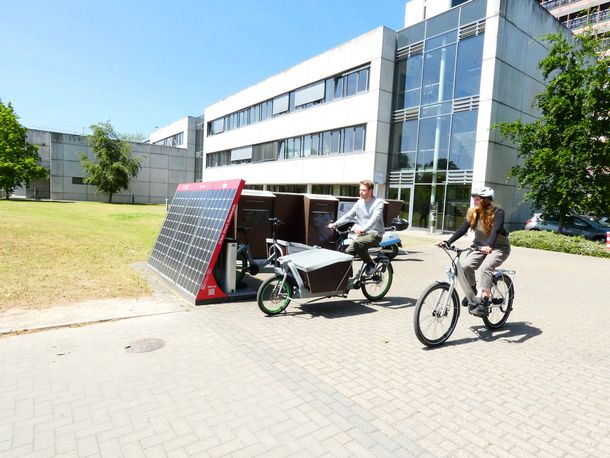


Project leader: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Semih Severengiz
E-scooters, e-bikes and the like now characterise the streetscape of many large cities in NRW. However, the use of these vehicles is not yet attractive for all citizens. E-micromobility could make a contribution to climate protection if business models work sustainably and economically. What are the problems? How can it become more widespread, especially in urban peripheral areas, and what increases acceptance? Methods such as spatial analyses, surveys of citizens and real-world laboratories should provide answers. In collaboration with an e-vehicle manufacturer and companies for battery exchange and solar charging stations, new business models are being trialled and evaluated with the help of real usage data. The project is based in the Laboratory for Sustainability in Technology.

Project Lead: Prof. Dr. Klaus Legner
Funding Source: Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF)
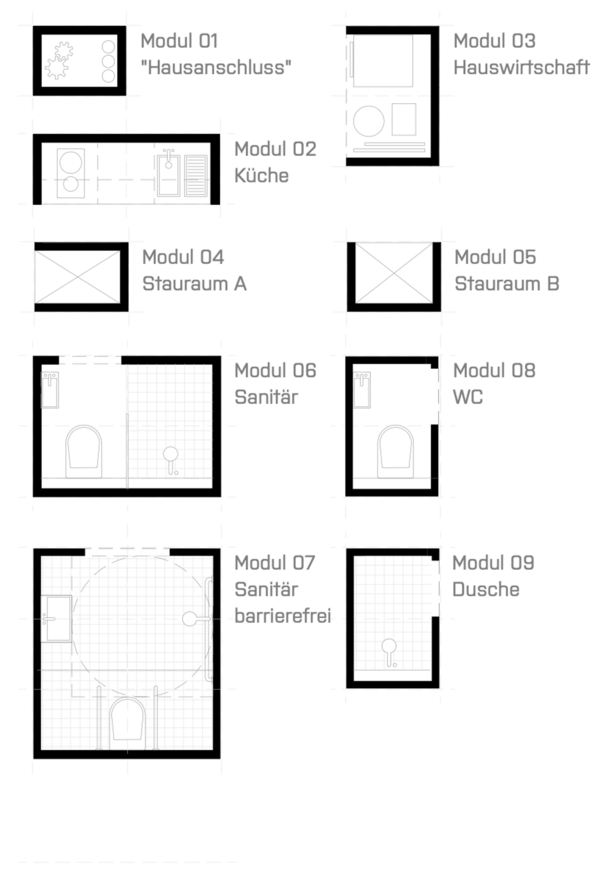
Anyone dreaming of home ownership often imagines a house or flat in the middle of nature, away from the city. This can be problematic, since urban sprawl means that cities continue to expand, (green) spaces are taken up and more traffic is generated, for example. It makes more sense to use existing areas in neighbourhoods and create good housing solutions. The "HABI-CORE" infrastructure core is designed for integration into vacant existing buildings and for small, unused gaps between buildings in the city. The aim is to create additional low-cost, affordable and accessible living space in urban areas. As part of the project, a sustainable prototype made of wood will be developed, built and tested and presented as a walk-in prototype in Bochum.
Project leader: Prof. Dr. Sven Pfeiffer
The aspect of sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the refurbishment and planning of buildings. Questions such as: Which form of insulation or heating is more sensible, more social, more economical? To find answers more efficiently in architectural planning, the Department of Architecture is working on a digital planning method that models building data in advance.


Project Leadership: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Semih Severengiz
Funding Provider: EU Commission
Duration: 06/2022 – 05/2026
Innovative Vocational Education in the Energy Transition Era SEED (Sustainable Energy Education) is a collaboration between five European regions, led by the Utrecht University of Applied Sciences, aiming to create a fossil-free continent through excellent, innovative vocational training.
SEED advocates for education's critical role in fighting climate change and transitioning to green energy. The project fosters collaborative development of superior energy education among vocational institutions and regional players, with goals to increase qualified professionals, integrate study programmes with job markets, and advance new energy technologies.
The initiative establishes five Centres of Vocational Excellence across the Netherlands, Finland, Spain, Germany, and Greece, forming an international community sharing standards and insights in sustainable energy education.
Additionally, SEED, part of the CoVE programme funded by the EU's Erasmus+, equips individuals with future-oriented skills and bolsters regional innovation. It supports best practices in teaching, industry partnerships, and educational management to enhance vocational education's appeal.
CoVEs, introduced by the European Commission, are networks that update vocational practices and offer quality skills training, linked to regional development strategies to foster new synergies and knowledge creation.

Project leader: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Andrej Albert & Thilo Schmidt, M.Sc.
Funding provider: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK)
Duration: 2022 – 2025
Co-op partners: fischerwerke GmbH & Co. KG, Ruhr-Universität Bochum and RWTH Aachen
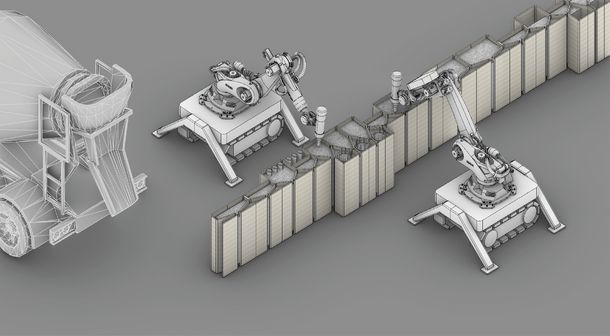
The objective of the "air-Kon-Matrices" initiative is to develop inflatable, individually shaped, resource-efficient hollow chamber matrices for the production of lightweight foundations. These matrices are intended to be incorporated into the formwork of foundations to selectively displace excess concrete, thereby significantly reducing energy consumption and associated CO2 emissions.
The responsibility for optimizing the form of the hollow chamber matrices lies with the Department of Solid Construction at Hochschule Bochum. This entails computational proof of load-bearing capacity through nonlinear FEM simulations and the application of an algorithm based on genetic programming.
A schematic depiction of an 'air-Kon foundation plate' under typical load conditions with tailor-made hollow chamber matrices is illustrated in the accompanying figure.

Project Leadership: Prof. Sven Pfeiffer
Funding Provider: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK)
Duration: 2022 – 2025
The objective of the 3DLight_OnSite project is to reduce CO2 emissions in the construction industry by developing a consistently CO2-optimized digital workflow for manufacturing multifunctional lightweight components with graded properties. The main innovation lies in introducing lightweight construction in the building sector through the conceptualization, development, and testing of in-situ manufacturing in additive manufacturing. Materials and digital planning methods are being developed for personalized, multifunctional lightweight components manufactured using robot-assisted additive processes. The project bridges the gap between fundamental research and industrial application by testing and validating the results with reference components from practical applications.
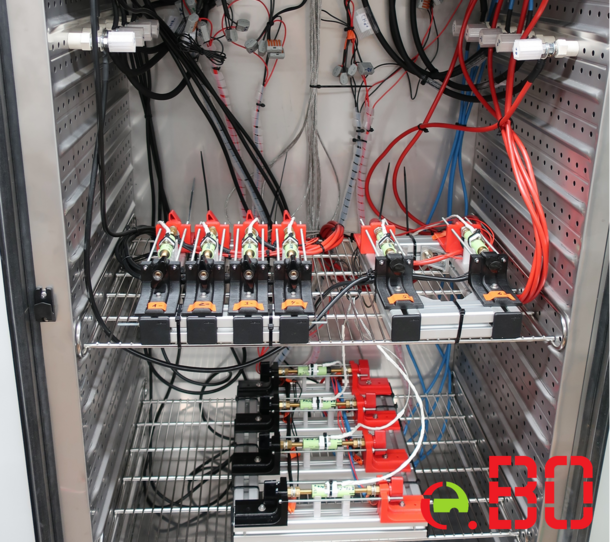

Project Leadership: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Friedbert Pautzke
Funding Provider: Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), "Battery 2020 Transfer" initiative
Duration: 11/2022 – 11/2025
Co-op partners: Neue Effizienz gGmbH (an institute of the University of Wuppertal) and the Chair of Electric Mobility and Energy Storage Systems at the University of Wuppertal
UniZuB focuses on developing, testing, and optimizing software and hardware solutions for assessing the health (State of Health; SOH) of high-voltage batteries (HV batteries), combining computer simulations and practical experiments for field application.
The state estimator, also referred to as a diagnostic tool or battery tester, will be developed over three years in collaboration with industry and research partners, using the transdisciplinary Design Thinking method. Key industry participants include AVL DiTEST GmbH, specializing in HV system measurement equipment, and Zweidenker GmbH, experts in cloud solutions. The project also involves AWG Abfallwirtschaftsgesellschaft mbH Wuppertal, interested in the tool for decisions regarding "Second-Life vs. Recycling" for HV batteries.
The project aims to:
- Develop a fast, reliable, adaptable methodology for estimating the state of HV batteries.
- Create a demonstrator for a universal rapid diagnostic device for HV batteries, including feasibility proof.
- Develop cloud solutions for storing various types of data.
- Realize a sustainable value chain for HV batteries (Circular Economy).
- Facilitate knowledge and technology transfer for lifecycle assessments of HV batteries.
- Establish a uniform methodology for hazard assessment in transporting electric vehicles and battery recycling.
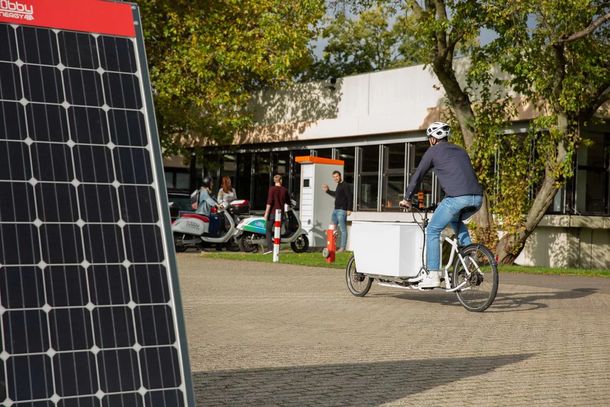


Project Leadership: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Semih Severengiz
Funding Provider: Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF)
Duration: 07/2022 – 06/2024
The transportation sector is undergoing a major transformation, focusing on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants, and developing digital, smart solutions for resource and land efficiency in urban areas. Solutions must be sustainable and affordable. Light Electric Vehicles (LEVs) like e-scooters, pedelecs, cargo bikes, and e-mopeds are key to achieving energy-saving, emission-free urban mobility.
The project explores sustainable energy supply for LEVs, addressing the challenge of integrating these vehicles with renewable energy sources using digital solutions. It builds on the SCiSusMob I subproject, emphasizing a holistic approach to mobility and energy from a sustainability perspective, incorporating future-proof digital infrastructure. The aim is to test and validate research findings in a real-world laboratory, focusing on a unified platform for mobility and energy services. This leads to a standardized methodology for evaluating the sustainability impact of mobility services.
Key research areas include:
- Developing sustainability assessment methods like Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and acceptance studies.
- Investigating energy supply concepts for LEVs.
- Creating business and operating models for mobility and energy services.
- Designing a decentralized digital platform for these services.
- Trialing the mobility and energy system in a real-world setting.
- Establishing standards and legal frameworks.
Led by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Semih Severengiz, the project is a collaborative effort with companies in the energy and mobility sectors, supported by firms like e-bility GmbH, Stadtwerke Bochum Holding GmbH, and others providing third-party funds.


Project Leadership: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Semih Severengiz
Funding Provider: Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF)
Duration: 12/2020 – 11/2024
The InnoVET project "UpTrain" focuses on revitalising vocational education in the mobility industry's commercial-technical sector. Addressing the need for 100,000 additional qualified staff in public transport by 2025, the project responds to challenges in digitalisation, electrification, and automation.
"UpTrain" aims to improve the permeability and attractiveness of industry-specific education through digital learning materials for a Mobility Academy and tripartite advanced training programmes linking transport companies, universities, and industry. The project will develop and test comprehensive further education models for the public transport sector.
Bochum University of Applied Sciences’ Laboratory for Sustainability in Technology will enhance cooperative learning sequences in energy, new mobility solutions, and scenario techniques, integrating digital content with blended learning approaches. The university also contributes to cross-institutional educational advisory services and participates in project evaluation and dissemination.
Partners include:
- VDV Academy e.V. (Association of German Transport Companies Academy e.V.)
- Cologne Transport Authority AG
- Rheinbahn AG
- Bergische Universität Wuppertal
- Bochum University of Applied Sciences
- Stadtwerke Verkehrsgesellschaft Frankfurt am Main mbH
- Rhein-Neckar-Verkehr GmbH
- Frankfurt University of Applied Sciences
- Hochschule Darmstadt – University of Applied Sciences
The project is funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) under the InnoVET initiative, executed by the Federal Institute for Vocational Education and Training (BIBB).
Project Leadership: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Friedbert Pautzke
Funding Provider: Federal Ministry of Education and Research, FH-Impuls programme
Duration: 04/2022 – 03/2024
This project involves designing a modular experimental vehicle and creating Digital Twins to develop a broad range of electric vehicle drive components, aimed at reducing integration efforts.
Project Overview
Objective: To generate a variety of combinable electric vehicle drive components, simplifying integration.
The OMAx-Vehicle project will develop a modular vehicle allowing for the integration and communication of electrical components from various manufacturers. Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) will be utilized for effective, solution-focused implementation, creating digital twins from existing mechatronic systems (OMEx-DriveTrain).
Key Outcomes:
- Modular vehicle design with drivetrain
- Application of MBSE
- Simulation models for digital twins
- Creation of digital twins for drive components
- Incorporation of fuel cell technology into OMEx-DriveTrain
- Hybrid testing and analysis with X-in-the-Loop
- Online educational materials and demonstrations

Project Leadership: Prof. Dr. Haydar Mecit
Duration: 07/2022 – 12/2024
Funding Provider: Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), FH-Impuls Programme
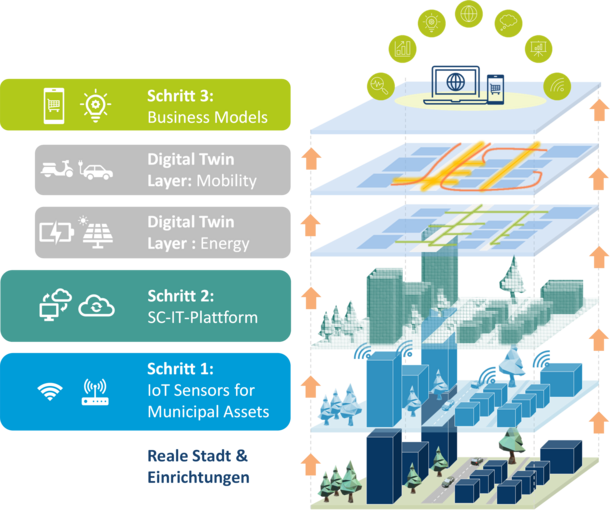
The main objective of the project is to advance and implement Smart City use cases in Smart Environment, Smart Mobility & Smart Energy as potentially replicable blueprints.
Building on previous studies, HpSCiLivLabs develops parts of a Smart City research lab as a collaborative space for various Smart City stakeholders. These workshops utilize data-driven simulation, prototyping, and Digital Twins approaches, bringing together participants from different sectors (like science, business, and local government) in an innovative work environment.
The focus is now on finalizing and expanding Smart City real labs (mainly sensors and data from urban spaces) previously set up for testing and validation. A central element is a partially existing and evolving Smart City IT platform, linking data sources from the real labs with the research lab. This platform will facilitate further processing and analysis of data to enhance Smart City use cases in environment, mobility, and energy, using modern visualization and collaboration methods.
Project Consortium:
- Bochum University of Applied Sciences, Institute for Electric Mobility and Laboratory for Sustainability in Technology
- FH Dortmund
- Westphalian University of Applied Sciences Gelsenkirchen, Institute for Internet Security
Industry and Public Institution Participants:
- Stadtwerke Herne AG
- Straßenbahn Herne-Castrop-Rauxel GmbH
- Wirtschaftsförderungsgesellschaft Herne mbH
- City of Herne, Digitalization Office


Project Leadership: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Semih Severengiz
Funding Provider: Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety (BMUV) (project reference: FKZ 67EXI4011A)
Volume (in €): 397.382
Duration: 08/2020 – 03/2023 (Extended)
MoNaL aims to establish sustainable mobility solutions for Sub-Saharan African countries. The project comprehensively considers the entire lifecycle impact – from vehicle production and design to energy supply and recycling of vehicles and energy infrastructure. A pilot implementation in Ghana, at the site of local partner Don Bosco, involves testing an electric moped and cargo bike rental system. This initiative adapts to local conditions and user requirements. Sustainable mobility is integrated with renewable energy, leading to the development of a smart mini-grid powered by independent solar installations and charging stations.
The mini-grid, part of the project, features automatic billing, enabling real-time adjustments of electricity prices based on factors like supply, demand, weather, and battery levels. The goal is to intensify the use of sustainable mobility alternatives while considering reliable and sustainable energy access. Addressing the issue of e-waste in the target country, the project incorporates the end-of-life phase of the developed product system. It involves analyzing existing recycling structures in Ghana, exploring options for second-life applications of solar modules and batteries, organizing workshops with local stakeholders to develop environmental standards, and conducting training in recycling and upcycling. Qualification measures in e-mobility, solar technology, and recycling ensure the sustainable use of the product.

Project Leadership: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Iris Mühlenbruch
Funding: North Rhine-Westphalia State for Connected Mobility and Mobility Management (FöRi-MM)
Duration: 2021 – 2023
The "Stadt Terrassen" project focuses on transforming street spaces into social hubs, play areas for children, and promenades. This initiative, supported by the Zukunftsnetz Mobilität NRW's loan offer of urban furniture, invites cities in North Rhine-Westphalia to temporarily redesign street spaces up to 150 meters, particularly repurposing areas used for car parking. The project aims to enhance the quality of stay and greenery in streets through modular systems. Citizens are encouraged to use the seating and reclining elements, revitalizing streets. Additionally, local participation processes are implemented to engage in dialogue with residents and visitors.
Bochum University of Applied Sciences is responsible for monitoring and evaluating the temporary use of the Stadt Terrassen. Various scientific methods will be used to investigate the following aspects:
- Impact and acceptance: How well is the urban furniture accepted by different user groups? What are the effects of using Stadt Terrassen?
- Formative aspects: Is the urban furniture practical, and what improvements or expansions can be made?
- Process evaluation: Identifying barriers and success factors in implementation, and developing recommendations for future projects.
Further Information:Zukunftsnetz Mobilität NRW website
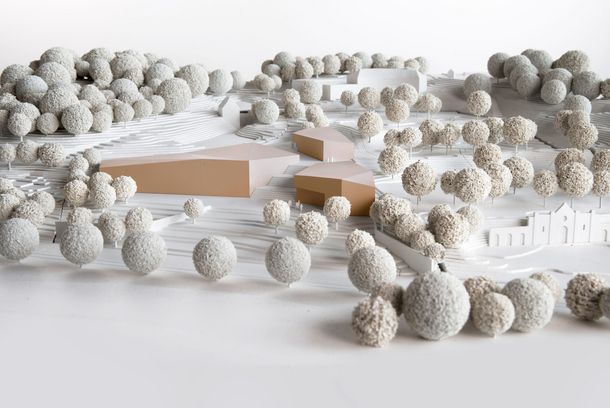


Project Leadership: Prof. Volker Huckemann
Funding Source: Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt [DBU]
Duration: 2019 – 2023
Museums, with their strict conservation requirements, are climatically demanding buildings, often leading to energy-intensive solutions. The Landschaftsverband Westfalen-Lippe (LWL) is planning a new entrance and exhibition building for the Freilichtmuseum Detmold, Germany's largest open-air museum. The project aims for a sustainable, life-cycle cost-oriented design, serving as a model for German architectural culture.
An interdisciplinary consortium, including architects, building climate experts, energy technicians, and educational scientists, will develop an innovative museum concept. The project comprises two phases: firstly, creating a guideline for building materials, technical equipment, and energy concepts, including a monitoring system for the new construction. This phase also focuses on the interplay between conservation requirements and energy needs, emphasizing adaptive components responsive to the museum artifacts' climatic tolerance limits. The findings will be shared with the public, particularly planners and investors.
The second phase will focus on knowledge transfer about sustainable, resource-efficient construction. Considering the diverse visitors to Freilichtmuseum Detmold, the project places a high educational value on museum pedagogy, aiming to reflect these values in the new building's design.
Further Information:
Project Leadership: Prof. Volker Huckemann
Funding Source: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi)
Duration: 2020 – 2023
Georg-August-University in Göttingen is transforming a 19th-century university building, listed for historical preservation, into the "Forum Wissen," a combined teaching, research center, and museum. Since January 2020, the building is being comprehensively renovated to suit its new function while preserving its historical appearance.
A key aspect of the renovation is meeting the museum's specific conservation requirements for room climate. To protect against solar radiation without altering the building's external appearance, Merck's switchable glazing is being installed. This technology ensures natural color rendition inside and contributes to a suitable climate for both exhibits and visitors, maintaining the building's original look.
The project includes researching the pilot use of switchable glazing in a museum setting. This involves achieving climatic requirements and assessing energy differences compared to traditional shading solutions.
The project's success is measured through thermal simulation, using TRNSYS software to model a museum section and simulate the switchable glazing. After validating the model with extensive climate and building technical parameters, it will serve as the basis for investigating the glazing's pilot use and optimizing the museum's technical operations.
Project Leadership: Prof. Dr. Haydar Mecit
Funding Provider: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWi)
Duration: 2020 – 2023
SEGuRo drives the development and testing of novel, digital energy solutions in urban spaces, focusing on the safe digitalisation of a section of the electricity grid in Herne's real environment. This transformation into a Smart Grid involves stakeholders from business, science, and the public sector, emphasizing secure, critical energy infrastructures.
With increasing integration of distributed generators (like photovoltaic systems) and loads (like electric cars and heat pumps), the project addresses the dynamic and unpredictable network behaviour in distribution grids. It innovates in distribution network monitoring, enabling a holistic system understanding, and develops a SEGuRo concept comprising tamper-proof data signing at measurement points, secure data transmission, and a real-time monitoring platform. This platform combines a digital twin, dynamic network state estimation, data management, and visualisation - a comprehensive innovation in network monitoring.
The project's objective is to create a digital twin based on detailed system modelling, supporting real-time network operation and compatible testing of new regulatory strategies or components before field integration. Bochum University of Applied Sciences, with its long-term partner Stadtwerke Herne AG and the SEGuRo research consortium, focuses on IoT & ICT possibilities in Herne's network area. The university's main tasks include scenario and requirements definition for secure, smart grids, and collaborating on a real-time platform for network monitoring and control in Herne. The project also emphasises Smart Grid field tests and research on monetising Smart Grid-based network services, aiming to explore future monetary potentials of technically feasible Secure Smart Grids in the context of Smart Energy.
The Real Lab Herne, led by Bochum University of Applied Sciences, will serve as a prototype and blueprint for other regions in Germany and internationally, supporting and helping to implement the energy transition elsewhere.

Project Leadership: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dirk Eling
Funding Provider: European Regional Development Fund (ERDF)
Duration: 07/2020 – 03/2023
Co-op partners: District Administration of Recklinghausen and the University of Duisburg-Essen's Institute for Construction Operation and Management
The construction industry, amidst challenges like housing shortages and sustainability demands, is leveraging technological advancements and digitalization for innovation. In the Ruhr metropolitan area, the pressure for innovation is heightened due to urban transformation and the need for sustainable solutions.
The project focuses on the implementation of Building Information Modeling (BIM). BIM provides a significant opportunity for more efficient and sustainable renovations, especially in the face of a renovation backlog in the region.
Key aspects of the project include creating detailed BIM models from diverse existing data and integrating quality and origin metadata. These efforts aim to enhance the local construction industry's competitiveness and efficiency, facilitating knowledge transfer from academia to practice and contributing to sustainable urban development. BIM's implementation will not only improve resource efficiency but also bolster economic and social sustainability by enabling cost-effective public construction projects, potentially aiding socially disadvantaged groups.

